- COMP.CS.140
- 2. Welcome to Programming 3: Interfaces and Techniques
- 2.3 Java: Programming Environment
Java: Programming Environment¶
Learning Outcomes
We will get to know the programming language used on the course, Java, and the programming environment needed. We will also discuss why the programming language used on the course is Java. After the section you are able to set up a Java programming environment for your course work and write and execute a simple Java-program.
Why Java?¶
It is likely that you have started learning programming with Python. In Tampere University Programming 1 uses Python and Programming 2 C++. Why does Programming 3 use yet another programming language instead of the earlier ones?
Python and C++ are useful to anyone in the field of Computing but it is good for a software developer to have experience in a wide range of programming languages. Additionally, Java is one of the most popular programming languages globally. The TIOBE index lists the most popular languages monthly, and Java has for a long time been one of the most popular languages on the list.
However, the most important reason for choosing Java is its suitability for studying the learning outcomes of the course. Java is platform independent meaning it aims at being a “write once, run anywhere” high-level programming language. Java is also an object-oriented language and thus provides an opportunity to study the key topics of the course directly through the structures provided by the programming language itself. The syntax of Java is similar to C++ and C and is thus relatively easy to learn at this point in your studies. Java also offers a rich collection of software components in the Java class libraries or Java APIs. It is both useful professionally and its features are ideal for the purposes of the course.
Java JDK¶
In order to implement Java programs you’ll need a Java compiler (javac) and a Java interpreter (java). We will get to know these in more detail a little bit later but let’s first set up the basics so we can start coding. Both the interpreter and the compiler are a part of the Java Development Kit (JDK). The JDK is a development environment for building applications and components with Java. It includes tools for developing and testing Java programs and running them.
JDK is available on university computers and on the remote desktop servers. For your own computer you might need to install it.
Do not install the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). JRE is meant for end users and it can only execute Java programs with the Java interpreter, in other words, it lacks the Java compiler, among other things. You can install JDK on a computer that has JRE, since the JDK installer should be able to configure your computer so that the Java interpreter in JDK will be used instead of the one in JRE.
Installing the JDK¶
First let’s check if the JDK is already installed. You can do this by running javac -version and java -version on the command line.
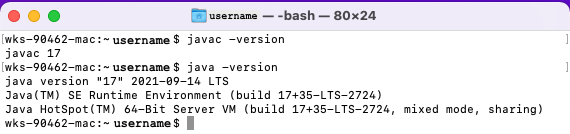
JDK 17 installed¶
The main versions of the JDK can be found on the Oracle web page. The latest version is 20. The Oracle Java License permits personal use and development use at no cost. In addition there is a fully free OpenJDK available under the GPLv2+CPE license. The latter is installed on the university environments.
The JDK is installed by selecting from the available options the one for your operating system and the appropriate package available for download. For Windows-users the easiest to use is the installation program, i.e. the file ending with .exe. For Macs the easiest is downloading the disk image, i.e. the file ending with .dmg. Detailed instructions for installation in different environments are available on the Oracle web page under Installation instructions.
A simple Java program can be written with a code editor into a code
file. For Java source code files the file extension is always .java. To compile and run a Java
program on the command line the commands
javac and java are needed. The former compiles the code into bytecode and the latter runs
the program. In practice an integrated development environment (IDE) is often used. In
addition to an editor and the compiler, an IDE contains other tools that help
with coding, such as a debugger. You may have come across IDEs such as
pyCharm and Qt Creator earlier in your studies.
IDEs suitable for Java development include Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio Code
and NetBeans, among others. Out of these the course has chosen to use
NetBeans as the example IDE, which we’ll introduce next,
as well as write our first Java program.